Gummy Stem Blight in Watermelon: Causes, Symptoms, and Control Methods
1. What is Gummy Stem Blight?
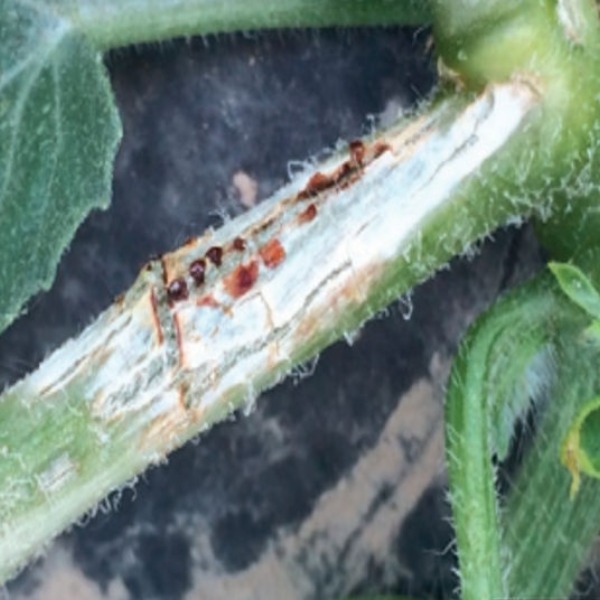
Gummy Stem Blight is a fungal disease that primarily targets the stems, leaves, and fruit of watermelon plants. It is known for the characteristic "gummy" that appears on infected plant tissues, especially on the stems and vines. This disease is prevalent in warm, humid conditions, making watermelon plants particularly susceptible during the summer months.
2. Causes of Gummy Stem Blight
• Fungal Pathogen: Didymella bryoniae is the primary pathogen responsible for Gummy Stem Blight. It thrives in moist, warm environments and spreads through soil, water, and infected plant material.
• Poor Crop Rotation: Continuous planting of watermelons or cucurbits in the same field year after year increases the risk of fungal buildup in the soil.
• Weather Conditions: High humidity, excessive rainfall, and temperatures between (24-29°C) provide an ideal environment for the fungus to thrive.
3. Symptoms of Gummy Stem Blight
• Dark, Water-soaked Lesions: Initially, small, dark, water-soaked lesions appear on the leaves and stems. These lesions often expand and become necrotic.
• Gummy Exudate: A characteristic sign of the disease is the "gummy" ooze that appears on the infected stems, often visible as a sticky, resin-like substance.
• Wilting and Yellowing: As the infection progresses, the plant may show signs of wilting, yellowing, and stunted growth.
• Fruit Rot: In severe cases, the fungus can infect the fruit, causing soft rot and rendering the watermelon unmarketable.
5. Control Methods for Gummy Stem Blight
Cultural Control:
• Crop Rotation: Rotate watermelons with non-cucurbit crops to break the disease cycle. A 3-4 year rotation can significantly reduce pathogen buildup.
• Sanitation: Remove and destroy infected plant debris at the end of the growing season. Clean equipment and tools to prevent cross-contamination.
• Well-Drained Soil: Ensure proper drainage in fields to reduce excess moisture, which favors fungal growth.
Chemical Control:
• Fungicides: Fungicides such as chlorothalonil, mancozeb, or azoxystrobin can be effective in preventing and controlling Gummy Stem Blight. Always follow recommended application schedules and dosages.
• Pre-Planting Seed Treatment: Use seed treatments to reduce the risk of introducing the pathogen into your fields.
Keywords
stems leaves
disease cycle
wilting yellowing
thrive 3 symptoms
watermelon plants
fungal disease
seed treatments
chlorothalonil mancozeb
34 year rotation
noncucurbit crops
severe cases
show signs
infection progresses
infected stems
characteristic sign
ideal environment
2429c provide
fungal buildup
year increases
field year
soil water
summer months 2
primarily targets
control methods 1
gummy ooze
characteristic gummy
infected plant tissues
reduce excess moisture
primary pathogen responsible
necrotic gummy exudate
gummy stem blight
moist warm environments