What is a Biopesticide?
A biopesticide is a type of pesticide that is derived from natural materials such as plants, animals, microorganisms, or minerals. Unlike conventional chemical pesticides, which are typically synthesized from chemicals, biopesticides are environmentally friendly and are used to control pests in a more sustainable way.
Types of Biopesticides:
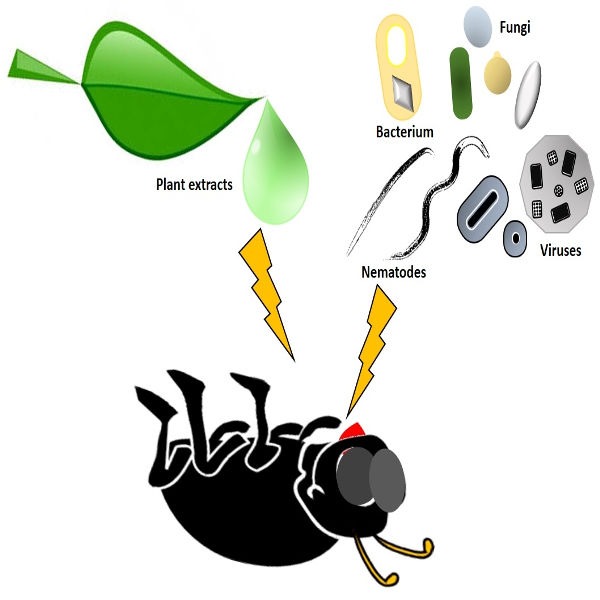
1. Microbial Biopesticides: These include naturally occurring microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, viruses, or algae that are used to control pests. For example, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a bacterium used to control certain insect larvae.
2. Plant-Incorporated Protectants (PIPs): These are substances produced by genetically modified (GM) plants that have been engineered to resist pests. For example, Bt crops like Bt corn produce a toxin that kills insect pests.
3. Biochemical Pesticides: These are naturally occurring substances, such as essential oils or plant extracts, that disrupt the pest\\'s behavior or life cycle. For example, neem oil, derived from the neem tree, is used to repel or kill pests.
Benefits of Biopesticides:
• Environmentally Friendly: Biopesticides are generally less toxic to non-target organisms (such as humans, wildlife, and beneficial insects) compared to chemical pesticides.
• Sustainability: They are often biodegradable and break down naturally in the environment, reducing the risk of long-term pollution.
• Specificity: Biopesticides are often more targeted to specific pests, reducing the risk of harming beneficial insects or animals.
Common Examples of Biopesticides:
1. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): A soil bacterium used to control a variety of insects, particularly caterpillars.
2. Neem Oil: Derived from the neem tree, this oil repels insects and works as a fungicide.
3. Trichoderma spp.: A fungus used to combat soil-borne diseases.
4. Insect Pathogens: Viruses and fungi, like Beauveria bassiana, which naturally infect and kill insects.
Keywords
soil bacterium
control pests
beauveria bassiana
humans wildlife
nontarget organisms
life cycle
plant extracts
essential oils
environmentally friendly
chemicals biopesticides
typically synthesized
natural materials
naturally infect
neem tree
pests behavior
resist pests
environment reducing
substances produced
bt crops
kill insects
neem oil derived
naturally occurring substances
specific pests reducing
kill pests benefits
bacteria fungi viruses
naturally occurring microorganisms
oil repels insects
harming beneficial insects
beneficial insects compared
bt corn produce
bacillus thuringiensis bt
animals common examples
chemical pesticides sustainability
plants animals microorganisms